This question is from Challenging Problems in Algebra
It’s the type of question students hate – “Who talks like that?”
Let ![]() be the number of hours from noon.
be the number of hours from noon.
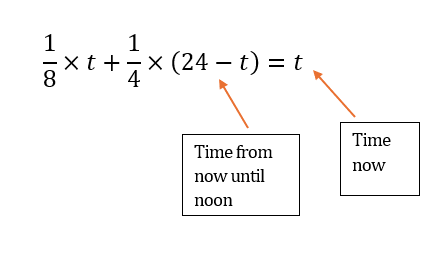
![]()
![]()
![]()
Hence the time is 5:20pm
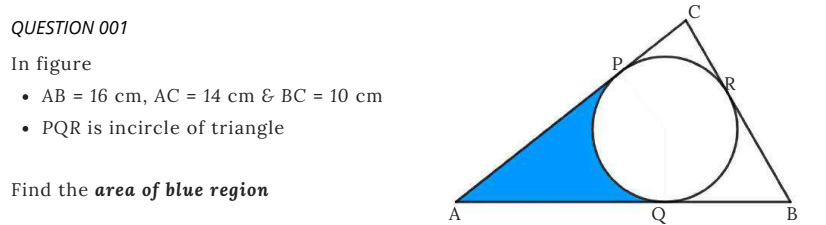
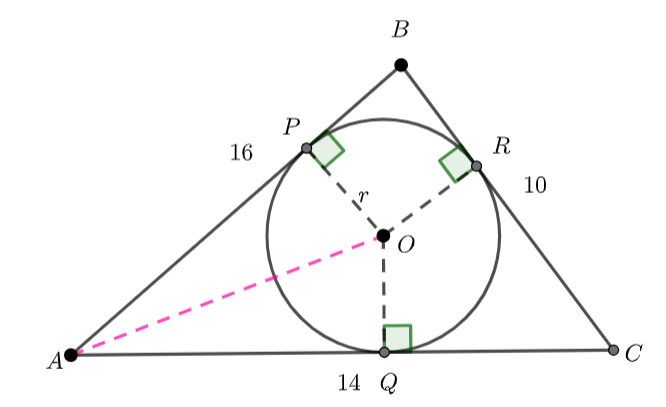
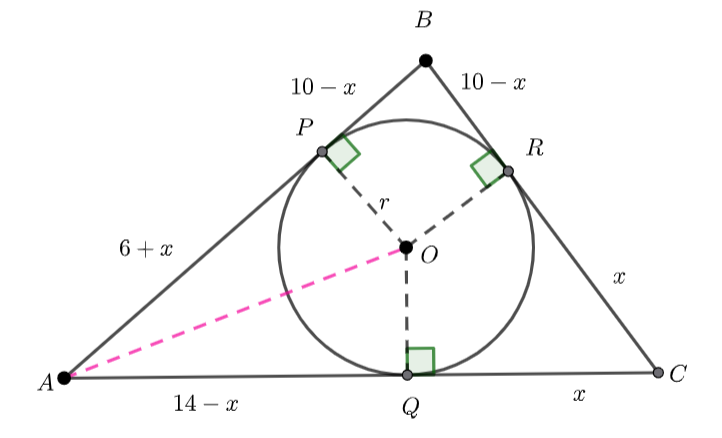
The blue shaded area is the area of triangles ![]() and
and ![]() subtract the sector
subtract the sector ![]() .
.
We can use Heron’s law to find the area of the triangle ![]()
![]()
where ![]()
![]()
We also know the area of triangle ![]() where
where ![]() is the radius of the inscribed circle.
is the radius of the inscribed circle.
Hence, ![]() and
and ![]()
We know ![]() , and
, and ![]() – tangents to a circle are congruent.
– tangents to a circle are congruent.
![]()
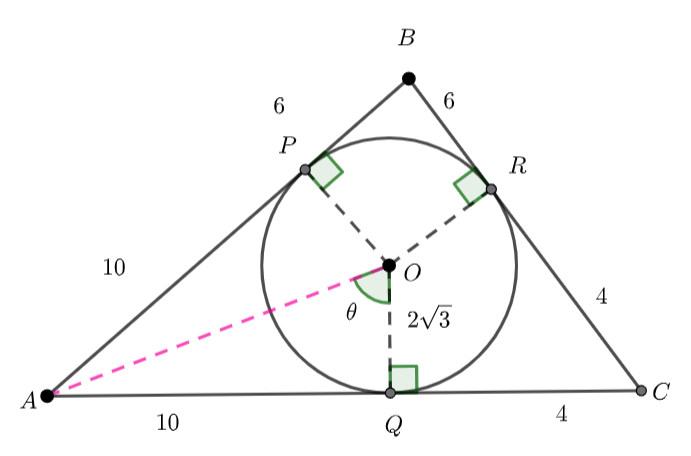
(1) ![]()
(2) ![]()
Area ![]()
Area ![]() Area
Area ![]()
![]()
![]()
Area of sector ![]()
Blue area = ![]()
Solve ![]() for
for ![]()
Remember the identity
(1) ![]()
Hence
![]()
Now I have
![]()
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]()
![]() for
for ![]()
![]()
![]()
Hence ![]()
I usually choose to use synthetic division when factorising polynomials, but I know some teachers are unhappy when their students do this. So for completeness, here is my PDF for Polynomial Long Division.
Find the value(s) of ![]() such that the equation below has two numerically equal but opposite sign solutions (e.g.
such that the equation below has two numerically equal but opposite sign solutions (e.g. ![]() and
and ![]() ).
).
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
For there to be two numerically equal but opposite sign solutions, the ![]() term of the quadratic equation must be
term of the quadratic equation must be ![]() .
.
![]()
Hence ![]() .
.
When ![]() the equation becomes
the equation becomes
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Filed under Algebra, Polynomials, Quadratic, Quadratics, Solving, Solving, Solving Equations
Find exactly ![]()
We must be able to find an arithmetic combination of the exact values we knew to find ![]() .
.
![]()
![]()
I re-arranged as above, so I could take advantage of ![]() and
and ![]()
| Useful identities |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Hence,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Use the quadratic equation formula
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
As ![]() ,
, ![]()
Two rectangular garden beds have a combined area of
. The larger bed has twice the perimeter of the smaller and the larger side of the smaller bed is equal to the smaller side of the larger bed. If the two beds are not similar, and if all edges are a whole number of metres, what is the length, in metres, of the longer side of the larger bed?
AMC 2007 S.14
Let’s draw a diagram

From the information in the question, we know
(1) ![]()
and
![]()
![]()
![]()
(2) ![]()
Equation ![]() becomes
becomes
![]()
As the sides are whole numbers, consider the factors of 40.
![]()
Remember ![]()
| Perimeter Large | Perimeter Small | Comment | ||||
| This one works | ||||||
| This one also works | ||||||
| Not possible | ||||||
Not possible | ||||||
| Not possible |
There are two possibilities
The large garden bed could be ![]() by
by ![]() and the smaller
and the smaller ![]() by
by ![]() (Area
(Area ![]() Perimeters
Perimeters ![]() and
and ![]() )
)
or
The large garden bed could be ![]() by
by ![]() and the smaller
and the smaller ![]() by
by ![]() (Area
(Area ![]() Perimeters
Perimeters ![]() and
and ![]() )
)
Solve ![]() for
for ![]()
Sine is positive in the first and second quadrants.
![]()
![]()
But what if we aren’t given a domain for the ![]() values?
values?
Then we need to give general solutions.
For example,
Solve ![]()
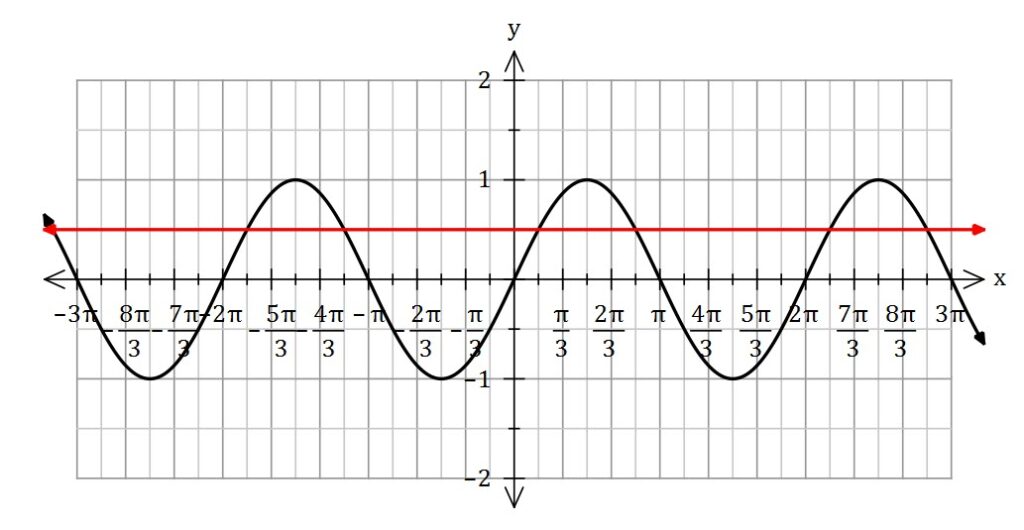
As you can see from the sketch above, there are infinite solutions.
The sine function has a period of ![]() , and so if
, and so if ![]() is a solution then
is a solution then ![]() is also a solution. This means
is also a solution. This means ![]() is a general solution. And we can do the same for the second solution
is a general solution. And we can do the same for the second solution ![]() .
.
In general
We can turn this into one equation
What about cosine?
Solve ![]()
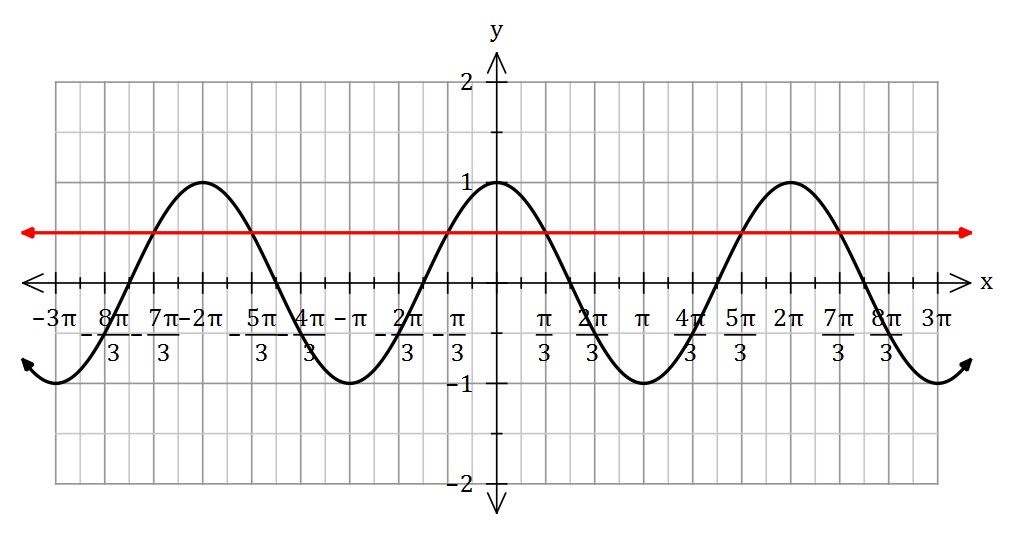
Cosine is positive in the first and fourth quadrants (it also has a period of ![]() . The first two (positive) solutions are
. The first two (positive) solutions are ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
To generalise, ![]() , which we can make into one equation
, which we can make into one equation ![]()
In general
What about the tangent function? Remember tan has a period of ![]() .
.
Solve ![]()
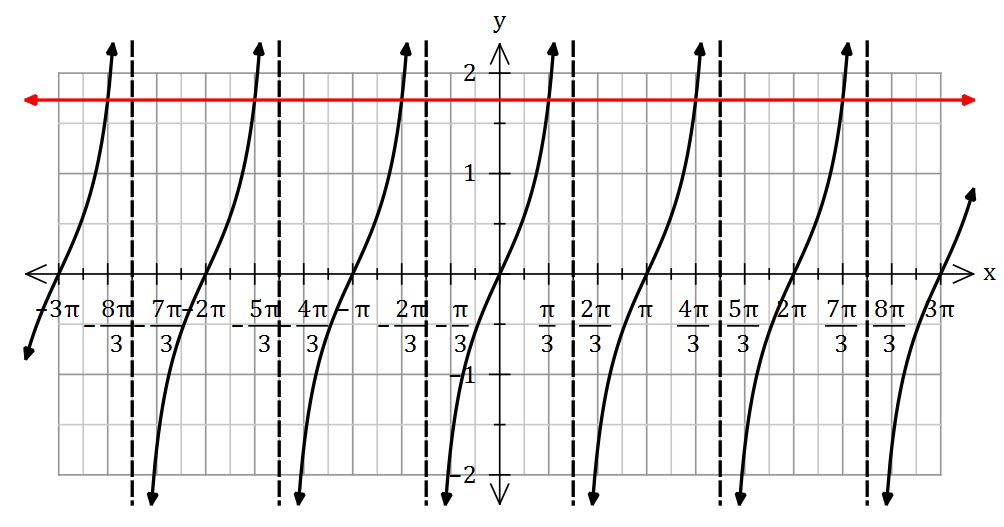
First, note that the solutions are all a common distance (![]() ) apart.
) apart.
Tan is positive in the first and the third quadrant
![]()
![]()
Because all of the solutions are ![]() radians apart, the general solution is
radians apart, the general solution is ![]()
In general
Solve for all values of ![]() ,
, ![]()
![]()
This is a quadratic equation – we need two numbers that add to ![]() and multiple to
and multiple to ![]() ,
, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solve ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Eight years ago my father was three times as old as I shall be in five years time. When I was born he was 41 years old. How old am I now?
I always find these age questions a bit weird – a bit of a riddle, and contrived (just so we can solve some equations)
Let ![]() be my age now, and
be my age now, and ![]() be my fathers age now.
be my fathers age now.
(1) ![]()
Because my father was 41 when I was born.
(2) ![]()
![]() for 8 years ago, and
for 8 years ago, and ![]() for three times my age in 5 years.
for three times my age in 5 years.
Solve the equations simultaneously. Substitute ![]() into equation
into equation ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Hence my current age is ![]() .
.